Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 Te
Te
Opletal, P.; Sakai, Hironori; Haga, Yoshinori; Tokiwa, Yoshifumi; Yamamoto, Etsuji; Kambe, Shinsaku; Tokunaga, Yo
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 92(3), p.034704_1 - 034704_5, 2023/03
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:57.37(Physics, Multidisciplinary)We investigate the physical properties of a single crystal of uranium telluride U Te
Te . We have confirmed that U
. We have confirmed that U Te
Te crystallizes in the hexagonal structure with three nonequivalent crystallographic uranium sites. The paramagnetic moments are estimated to be approximately 1
crystallizes in the hexagonal structure with three nonequivalent crystallographic uranium sites. The paramagnetic moments are estimated to be approximately 1 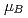 per the uranium site, assuming a uniform moment on all the sites. A ferromagnetic phase transition occurs at
per the uranium site, assuming a uniform moment on all the sites. A ferromagnetic phase transition occurs at  = 48 K, where the in-plane magnetization increases sharply, whereas the out of-plane component does not increase significantly. With decreasing temperature further below
= 48 K, where the in-plane magnetization increases sharply, whereas the out of-plane component does not increase significantly. With decreasing temperature further below  under field-cooling conditions, the out-of-plane component increases rapidly around T
under field-cooling conditions, the out-of-plane component increases rapidly around T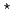 = 26 K. In contrast, the in-plane component hardly changes at T
= 26 K. In contrast, the in-plane component hardly changes at T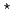 . Specific heat measurement indicates no
. Specific heat measurement indicates no  -type anomaly around T
-type anomaly around T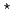 , so this is a cross-over suggesting a reorientation of the ordering moments or successive magnetic ordering on the part of the multiple uranium sites.
, so this is a cross-over suggesting a reorientation of the ordering moments or successive magnetic ordering on the part of the multiple uranium sites.
Amano, Hikaru; Uchida, Shigeo*
JAERI-Conf 2003-010, 394 Pages, 2003/09
The International Symposium : Transfer of Radionuclides in Biosphere, Prediction and Assessment was held at Mito on the 18th and 19th of Dec. 2002. This Symposium was organized by the Interchange Committee on Radionuclide Transfer in Soil Ecosphere. This project is the 3rd Phase Crossover Research, which is engaged in cooperation with five organizations:JAERI, MRI, NIRS, RIKEN and IES. The main objective of this symposium is to discuss and exchange recent findings and ideas in the area of the behavior and transfer of radionuclides in biosphere. One of the important topics in this symposium is to discuss a suitable transfer model and transfer parameters which may be adapted for Southeast Asian countries including Japan, as environmental conditions and foodstuffs in this region are significantly different from those in Europe and North America. The symposium consisted of 12 invited lectures and 44 poster presentations. The 120 participants attended the symposium, including 19 foreigners coming from 12 countries.
Uchida, Shigeo*; Amano, Hikaru; Takahashi, Tomoyuki*; Chiba, Masaru*; Hisamatsu, Shunichi*; Enomoto, Shuichi*; Matsumoto, Shiro*
JAERI-Conf 2003-010, p.25 - 31, 2003/09
In the 3rd Stage Crossover Research (1998 to 2003), a project on Development of a dynamic transfer model of radionuclides in the soil ecosphere,is currently being promoted. The following five researches are carried out in this project. 1) Research into the forms of existence of nuclides and their change in the soil (NIRS and JAERI), 2) Research into the transition behavior of radionuclides in plants (IES, RIKEN and NIRS), 3) Research into the relation to the microorganism and on environmental remediation (RIKEN, JAERI and NIRS), 4) Research on the migration of radionuclides from atmosphere to soil and plant (MRI and JAERI), and 5) Database construction on transfer parameters (JAERI, NIRS and MRI). JAERI, MRI and NIRS are working on the development of a dynamic transfer model such as MOGRA for radionuclides on the basis of a gained knowledge about the environmental behavior through cooperation with universities, etc. This model is also capable of the predicting the behavior of materials that are harmful to the environment such as hazardous heavy metals discharged in the soil ecosphere. In this presentation, we will overview the ourcome of the 3rd stage research.